Unlocking SharePoint Views and Filters: A Guide to Avoiding Subfolders
As organizations adopt SharePoint Online (SPO), users accustomed to folder-based systems often encounter a paradigm shift: transitioning from hierarchical folder structures to a flat, metadata-driven approach. While this may seem like a daunting change, the benefits of SharePoint’s views and filtering capabilities can transform how teams manage, access, and interact with their content.
This article explores why SharePoint views and filtering are game-changers, detailing how they compare to folder-based organization systems and offering actionable insights to leverage these features effectively.
From Folders to Flat: Why Change?
Folder-based systems rely heavily on hierarchical folder structures to organize content. While familiar, this approach has limitations:
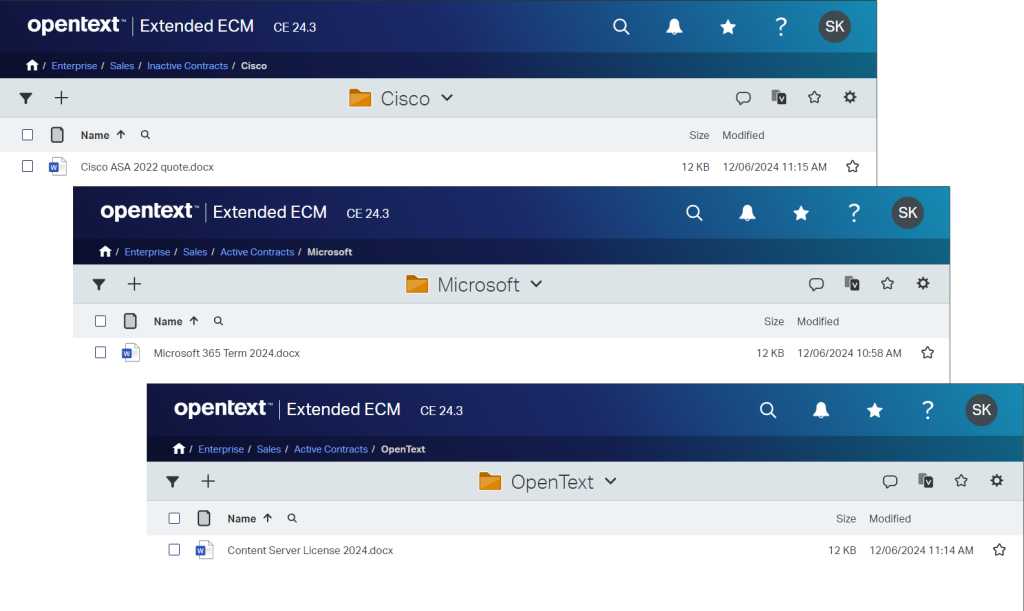
- Deep Navigation: Locating files buried several layers deep can be time-consuming.
- Limited Context: File names and folder titles often fail to convey enough information.
- Access Challenges: Folder permissions can become complex and error-prone as hierarchies grow.
SharePoint Online, by contrast, emphasizes metadata and tagging, encouraging users to focus on what a document is rather than where it lives. The shift to a flat structure, paired with powerful views and filtering tools, unlocks significant efficiencies.
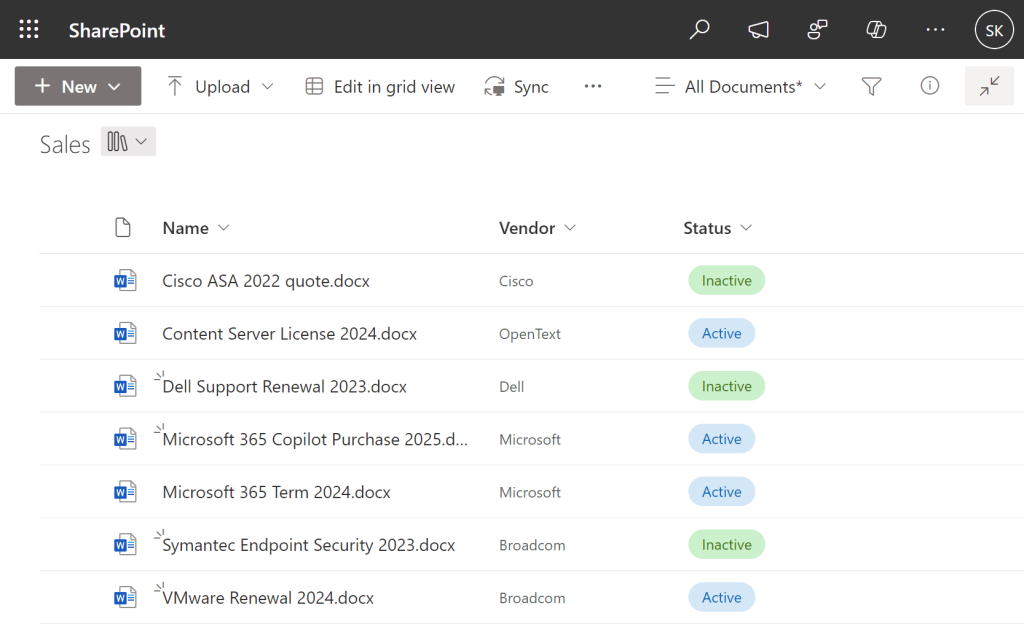
What Are SharePoint Views?
A view in SharePoint is a customizable way to display and organize content stored in lists or libraries. Instead of static folders, views dynamically group and present documents based on criteria you define, such as metadata tags, authors, or dates.
Key Features of Views:
- Dynamic Filtering: Display only the content that meets specific conditions without moving files.
- Customizable Columns: Tailor the displayed information to include only relevant fields.
- Personalization: Create personal views to match individual workflows while maintaining shared organizational standards.
- Group By Options: Automatically group related items under expandable headers, mimicking folder-like behavior but with more flexibility.
- Sorting and Formatting: Set default sort orders and apply conditional formatting to highlight key data points.
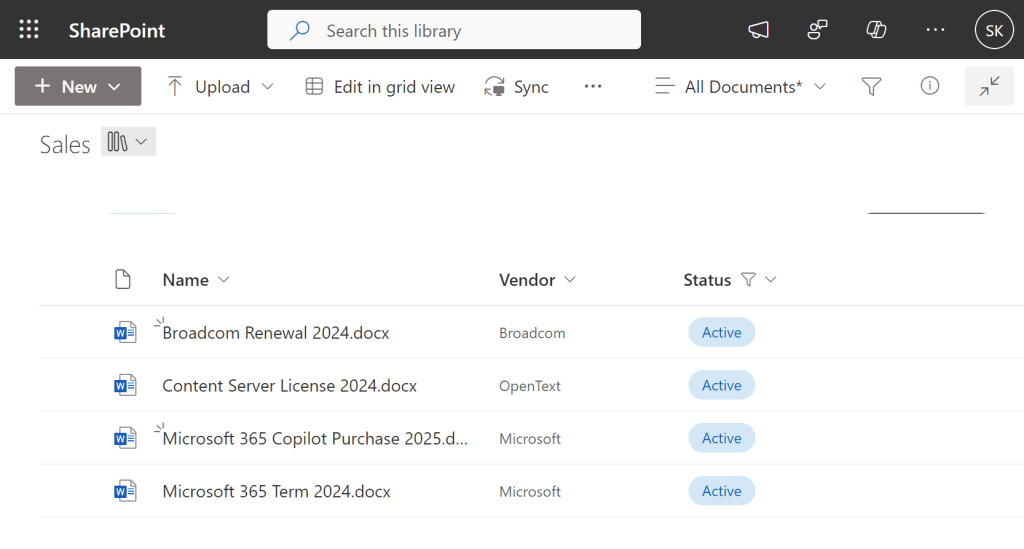
The Power of Filters in SharePoint
Filters refine how content is displayed within a view. Using filters, users can quickly narrow down massive datasets to find what they need—without altering the underlying structure.
Filtering Advantages:
- Instant Access: Locate relevant documents by applying one or multiple filters simultaneously.
- Multi-Tag Support: Unlike folders, filters allow content to be categorized by multiple criteria, making it accessible through various pathways.
- Saved Filters: Preserve frequently used filters as part of a view for easy reuse.
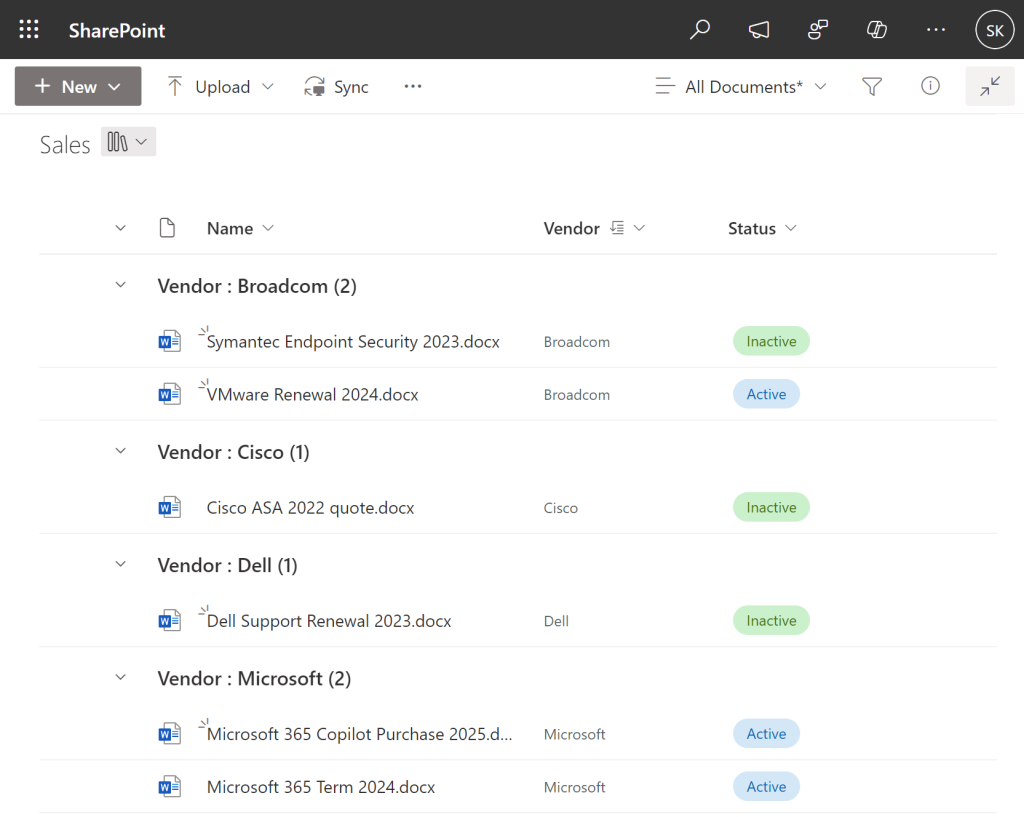
Why Views and Filters Outperform Folders
For users accustomed to folder-based systems, here’s a comparison to illustrate the benefits of SPO’s approach:
| Aspect | Folder-Based Organization | Views and Filters in SharePoint Online |
|---|---|---|
| User Experience | Linear and rigid; users must adapt to the folder structure. | Adaptive and tailored to individual workflows, enhancing productivity. |
| Flexibility | Static and hierarchical; content is locked into a single location. | Dynamic and metadata-driven; content can be organized and accessed in multiple ways without moving files. |
| Navigation | Requires navigating through multiple layers of folders to find documents. | Allows instant access to documents using filters, metadata, and customized views. |
| Scalability | Difficult to manage as the number of folders and levels grows. | Easily scales with metadata and filters, regardless of the number of documents. |
| Permissions | Complex and error-prone with deeply nested folders. | Simplified permissions at the document library level, with metadata providing additional flexibility. |
By leveraging SharePoint views and filters, your organization can streamline content management, reduce inefficiencies, and create a scalable system designed for modern collaboration needs. Embracing these features transforms document management into an intuitive and powerful experience.